Appium Interview Questions
What is Appium?
Appium is an open-source mobile testing automation tool that is used to test mobile applications. Sauce Labs created and supports it to automate hybrid and native mobile apps. It's a cross-platform mobile automation tool, implying that it can perform the same test on various platforms at the same time. Appium may simply test many devices in parallel. Mobile applications are in high demand in today's developing world. People are currently transforming their websites into mobile apps. As a result, it's critical to understand mobile software automation testing technology and to keep up with emerging technology. Appium is a mobile app testing solution that is now popular in the field of mobile automation testing.
Appium is a testing framework for native, hybrid, and web applications. It supports both simulators (iOS) and emulators (Android) as well as actual devices for automation testing (Android and iOS both). Earlier, this tool was limited to mobile application testing and solely focused on IOS and Android applications.

Appium is a testing tool that is quite similar to Selenium Webdriver (a web framework that allows executing cross-browser tests). Appium becomes incredibly simple to learn if you have prior knowledge of Selenium Webdriver. Appium has no Operating System dependency since it contains a framework that translates Selenium Webdriver commands to UIAutomator and UIAutomation commands for Android and iOS, which are dependent on device type rather than OS type.
Appium supports various languages, which have Selenium client libraries, such as Java, PHP, Objective C, C#, Python, JavaScript with node.js, Ruby, and many others. Selenium is the Appium backend that allows you to control Selenium's functionality for testing purposes.
In this article, we will discuss the most frequently asked interview questions on Appium.
Appium Interview Questions for Freshers
1. Explain the JSON Wire protocol used by Appium.
The JSON Wire Protocol is the method by which client and server data are exchanged. It was created by WebDriver's developers. The protocol, according to them, consists of a set of standardised endpoints that are offered to clients via a RESTful API. This enables the webdriver to communicate with a server and a client in order to automate tasks. In this protocol, JSON is used to transmit data between the server and the client. Before delivering an object to a server, a client (or the computer running the WebDriver API) turns it into a JSON object. The JSON object is parsed by the server and converted back to a JavaScript object. The response object is converted to a JSON string by the server and returned to the client. For use, the client transforms the JSON string to a JavaScript object.

In the above image, we can see the client and the server communicates with each other via JSON wire protocol. The server sends a request to the appium server for running tests and the appium server sends back the response to the main server.
The mobile JSON Wire Protocol, which is an extension of the Selenium JSON Wire Protocol, is used by Appium. Other than establishing up a communication stream, it's used to regulate other mobile phone behaviours.


 Real-Life Problems
Real-Life Problems
 Prep for Target Roles
Prep for Target Roles
 Custom Plan Duration
Custom Plan Duration
 Flexible Plans
Flexible Plans
2. What do you mean by Appium Package master? How would you create a package?
Appium Package master refers to a set of tools that are used to create and manage Appium packages.
To create a new Appium package, we can use the following lines of code:
//For es7/ babel
Gulp create-package -n <package-name>In the above code, we use Gulp (a streaming build system) and the command “create-package” to create a new package. -n signifies a new package has to be created and <package-name> signifies the name of the package to be created.
// For regular es5
Gulp create-package ---nobabe1 -n <package-name>In the above code, we mention --nobabel so as to specify that the command is for regular es5.
3. Is it possible to use JavaScript to interact with applications while running Appium tests?
Yes, we can use javascript to interact with applications while running Appium tests. When we perform the instructions on Appium, the server transmits the script wrapped in an anonymous function to our app, which is then executed.
4. Can a tester run tests in a multi-threaded environment while using Appium?
Yes, Appium allows testers to execute tests in a multithreaded environment. The only thing they have to worry about is that no more than one test runs against the same Appium server at the same time.
5. Explain Desired Capabilities in the context of Appium.
On iOS and Android, Appium behaves differently. Because it is a "cross-platform" tool, a method must be in place to distinguish between the session requests of the two operating systems. JSON objects, referred to as Desired Capabilities, were introduced to address this specific problem statement.

Desired Capabilities are key-value pairs of data that separate the establishment of an Android app testing session from that of an iOS app testing session. With arguments such as platformName, deviceName, appPackage, and appActivity, the server will be able to tell the difference between the two operating systems very quickly.
 Learn via our Video Courses
Learn via our Video Courses
6. Explain Appium Session in the context of Appium.
Appium session is a medium to send commands to a specific test application. Commands are always executed within the context of a session. Before performing any command, a client utilizes the session identifier as the sessionId parameter. A session is requested by the client library from the server. After that, the server will return a sessionId endpoint, which can be used to submit additional commands to interact with the application(s) being tested.
Every 'testing' is included within a session. Given that Appium is a simple client and server-based method, this is self-evident. Post requests, also known as session requests, are sent by the client to the server. These queries use the JSON Wire Protocol to communicate and convey information in JSON Object format.
7. What are the features of Appium?
Following are the features of Appium:-
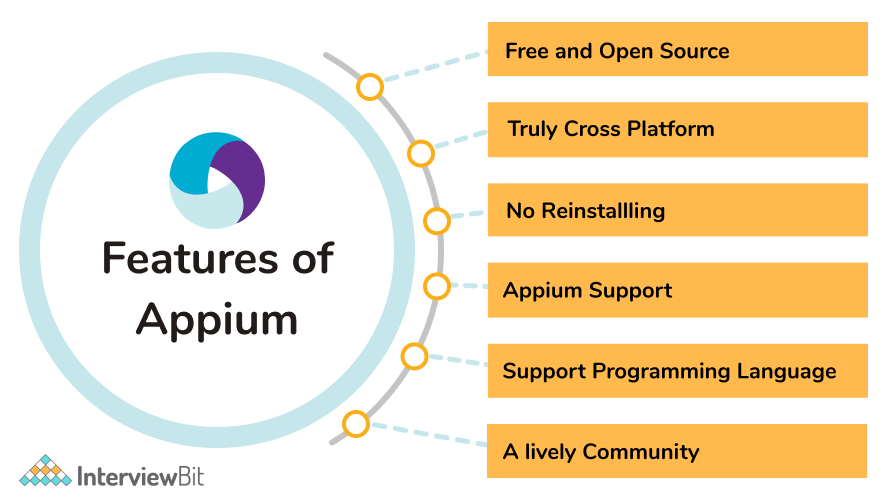
- Appium does not necessitate the use of an application's source code or a library.
- Appium has a vibrant and engaged community of developers and so help is easily available from the community.
- Appium supports multi-platform testing, which means it can execute the same test cases on several platforms like iOS mobile, Android mobile, and Windows desktop applications.
- Appium allows test scripts to run in parallel with other test scripts.
- A minor modification in Appium does not necessitate reinstalling the application.
- Appium supports a wide range of languages that use the Selenium client library, including C#, Python, Java, Ruby, PHP, JavaScript with node.js, and many others.


 Real-Life Problems
Real-Life Problems
 Detailed reports
Detailed reports
8. What is mobile application testing and how does it differ from mobile testing?
The practice of testing application software produced for handheld mobile devices for functionality, usability, and consistency is known as mobile application testing. Mobile application testing can be done in two ways: automated or manually.
It differs from Mobile Testing, Mobile Testing focuses on native application functionalities of mobile devices such as call, SMS, and media player, among others. Meanwhile, in Mobile Application Testing, we concentrate solely on a specific application's operation and end-to-end features.
9. What do you understand about end-to-end mobile testing automation? What things should be kept in mind while performing end-to-end mobile testing automation?
End-to-end mobile application test automation is a method of testing a software product from beginning to end to ensure that the application flow is as planned. It establishes the product's system mandates and ensures that all integrated components perform as expected.

The goal of end-to-end (E2E) mobile application test automation is to test from the perspective of the end-user by replicating a real-world situation, in which a user uses the application, and confirming the system under test and its components for data integrity and integration.
These days, software systems are sophisticated and integrated with numerous subsystems. The entire software system could fail if one of the subsystem fails. We employ end-to-end mobile application test automation to eliminate this big risk.
Following things should be kept in mind while performing end-to-end mobile testing automation :
- The installation of the application
- Launching the application for the first time without having network access.
- The uninstallation of the application.
- If the application is supported in horizontal mode, the orientation of the application.
- Testing the performance of an application on a variety of devices and network conditions.
- Testing the application's response and how it reacts when a user credential is provided that is invalid.
10. Explain the architecture of Appium.
Appium is an HTTP server implemented in the node.js programming language. It creates a server on the device and waits for proxied commands from the main Appium server. The test scripts are written by the tester and run on the device or emulator. Appium creates and manages many webdriver sessions for various platforms such as Android and iOS.
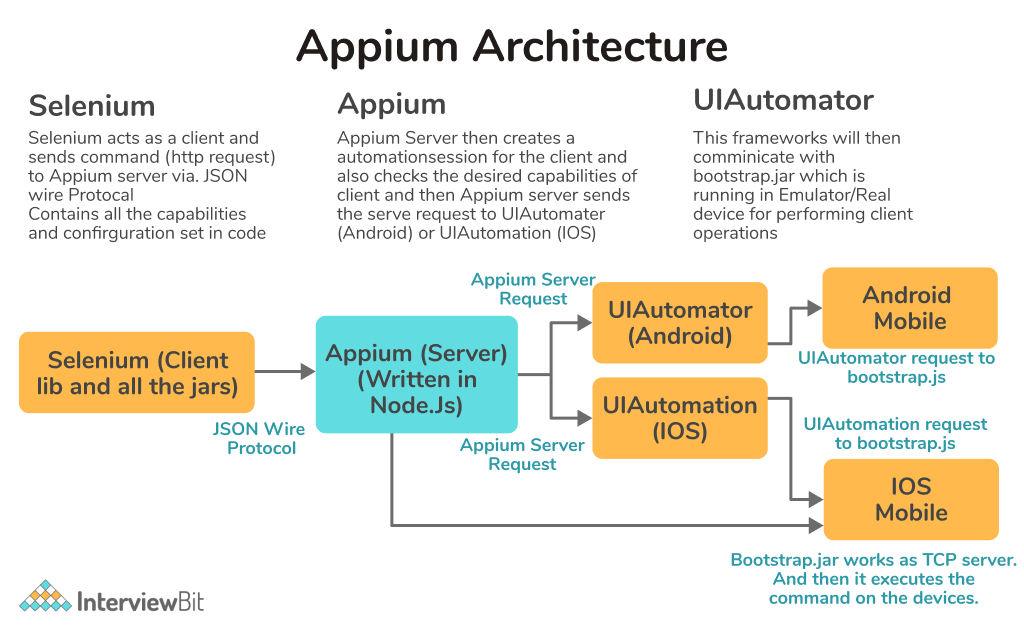
Test scripts produced by the tester are sent to the Appium server as requests, which are then executed on the emulator or device. Each vendor has its own technique and methodology for executing test cases on the device, such as IOS or Android. As a result, the test case runs after the Appium server receives commands. To transmit command requests to the Appium server, Appium uses JSON (Javascript Object Notation) wire protocol. Here, JSON is used to transmit data between the server and the client.
11. What do you mean by Appium Inspector?
Appium offers an "Inspector" to record and playback, similar to Selenium IDE's record and playback tool. It inspects the Document Object Model to record and play native application behaviour and provides test scripts in any preferred language. You can use the Inspector in Appium Desktop to look up or locate elements of an application.
To locate an element, the Appium inspector provides four options:
- To find elements by id
- To find elements by class name
- To find elements by accessibility id
- To find elements by xpath.
Appium Inspector does not support Windows and instead uses the UIAutomator viewer as an option.
12. List out the prerequisites required to run tests on an android application in Appium locally.
Following prerequisites must be installed so as to successfully run tests on an android application in Appium locally :
- Java Development Kit (JDK).
- Android Studio.
- Android SDK Tools.
- Eclipse IDE.
- Appium Desktop Client.
- TestNG.
- Selenium Server JAR.
- Webdriver Language Binding Library.
13. Explain the general responsibilities of a mobile application testing framework. Also explain the general structure of a mobile application testing framework.
Following are the general responsibilities of a mobile application testing framework:
- Choosing a format for expressing expectations
- Developing a means to connect to or control the test application
- Performing the tests and reporting the results
The general structure of a mobile application testing framework consists of the following segments :
- Application Package: This refers to the target application which needs to be run and tested.
- Instrumentation TestRunner: A test case runner that executes test cases against the target application. It includes an SDK tool for creating tests as well as an API tool, such as MonkeyRunner, that gives APIs for designing a program that controls an Android device.
- Test Package: Two classes, Test case classes, and Mock objects are included in the Test Package. The mock object contains mock data that will be used as sample input for test cases, while the test case classes contain test methods to run on the target application.

In the above figure, we can see that a mobile application testing framework consists of three segments: Application package, InstrumentationTestRunner, and Test package. The test package consists of mock objects, test case classes, and Instrumentation and JUnit classes.
14. What are the major advantages of using Appium on Sauce Labs rather than using Appium locally?
Following are the advantages of using Appium on Sauce Labs rather than using Appium locally:
- It saves us the time that it takes to set up the Appium server locally.
- We do not need to install the mobile emulators and simulators offline in our system. We can directly use it on Sauce Labs (an American cloud-hosted web and mobile application automated testing platform company based in San Francisco, California).
- It lets us scale our application instantly.
- We do not need to make any modifications to the source code of our application as is the case while using Appium locally.
15. What types of tests are suitable for Appium?
There are many scenarios that can be tested when it comes to testing, especially for web applications, depending on the feature coverage you want to assure. Appium comes in helpful when it comes to testing scenarios that users will encounter when using your app.
Appium, on the other hand, becomes a restriction if you need to test more than UX simple interactions. Consider features such as keyboarding. When sophisticated touch/keyboard mixed circumstances are involved, the likelihood of a false failure is significant. Exchanging data is another minor pain with Appium. You'll need to use various strategies when your test needs to exchange data with your app. So keep in mind that sending and receiving information isn't always simple. It's not Appium's fault; the WebDriver specification was created to automate processes, not data exchange.
16. Do you need a server machine to run tests on Appium?
No, we do not need a server machine to run tests on Appium. Appium encourages a two-tier architecture, in which a test machine connects to a test server that runs Appium, automating the entire process. This setting is optional; you can run Appium on the same system as your tests. Instead of connecting to a remote host, your test will use the loopback address to connect to Appium.
17. What are some of the important mobile application testings?
Following are some of the important mobile application testings:
-
Usability Testing: Usability testing is one of the sorts of web application testing that is perfect for assessing how the application makes it easier for users to achieve their goals. During this test, participants are given particular, realistic circumstances to use the application in. On the basis of gathering direct input from the end-user, usability testing is also reliable.
As a result, the testing procedure is free of prejudice while simultaneously guaranteeing that highlighted areas improve. Usability testing also ensures that the design is intuitive and prioritises usability and customer experience. -
Performance Testing: Performance testing is a critical subset of mobile application testing that examines an application's performance, stability, and responsiveness under various workload situations. A performance test's main goal is to ensure that an application is completely aligned with the performance objectives.
Additionally, it addresses performance constraints prior to launching an application. Bottlenecks are processes inside a system's overall functions that cause the system's overall performance to slow or stall. Load testing, volume testing, soak testing, spike testing, and stress testing are all popular forms of performance assessments. -
Security Testing: In today's world, security is a major worry for practically every mobile application developer. According to reports, 80% of users are more likely to delete an application because of security concerns. As a result, it is critical to concentrate on mobile application security testing.
Users' personal information is required by certain programs, such as travel applications, for various transactions. If your application requires something similar, it's critical that you provide assurances about the application's confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity. You should have strong tests run on your application that assure that no one can break into someone else's account by unfair means. - Interruption Testing: Interruption testing is important for determining how an application behaves when it is interrupted before returning to its former state. Incoming phone calls or SMS, alarms, push notifications from mobile applications, battery low or full, network connection loss and recovery, and plugged in or out while charging are all examples of interruptions. In the event of an interruption, an application should normally run in the background and return to its prior state.
- Manual Testing: Manual testing is a tried and true method for thoroughly traversing the complexity of mobile application testing. Manual testing ensures that the finished product performs optimally in accordance with the planned expectations. It's especially useful in situations where the use case isn't immediately evident. Professional QA testers could work in short bursts to assess an application and ensure that it produces accurate results.
-
Compatibility Testing: Compatibility testing is one of the most important types of mobile application testing. It's a form of non-functional testing that ensures a mobile application's functionality across a variety of operating systems, applications, devices, internal hardware specs, and network conditions. Compatibility testing determines whether a mobile application is compatible with various operating systems and versions.
It also tests a mobile application's compatibility with various devices, browsers, networks, and other characteristics. Backward compatibility testing and forward compatibility testing are the two types of compatibility testing. - Localisation Testing: Localization testing is a must for mobile applications that are targeted at a certain geographic location. It's crucial to test the mobile application's responsiveness to the region's distinct language and cultural aspects. Local currency, use of suitable time zone date and time formats, numerous local legislation needs, and the text and user interface are only a few of the important areas that localization testing evaluates.
- Functional Testing: Functional mobile application testing ensures that the application's functionalities meet the specified requirements. This form of testing focuses mostly on the mobile application's main goal and flow. Functionality testing determines if an application can properly launch and install. It also tests the simplicity of sign-up and login, as well as the presentation of push notifications and the proper operation of text boxes and buttons.
- Installation Testing: Installation testing, also known as implementation testing, is a good way to ensure that a mobile application is installed and removed correctly. Furthermore, installation testing is necessary to ensure that updates are seamless and error-free. Installation testing also examines what happens if users fail to update a mobile application.
- Automated Testing: Certain mobile application quality assessments are overly complicated and time-consuming. In such instances, Mobile application Test Automation Services come into play, providing optimally prepared and effectively conducted automated testing as well as manual testing, which can aid in assuring quality while also allowing for the speedier release of superior goods. As a result, automated testing is a solid source of time and cost savings when it comes to mobile application testing. There are various tools to perform automated testing. Appium is one of them.
18. What are the different types of mobile applications?
Following are the different types of mobile applications:
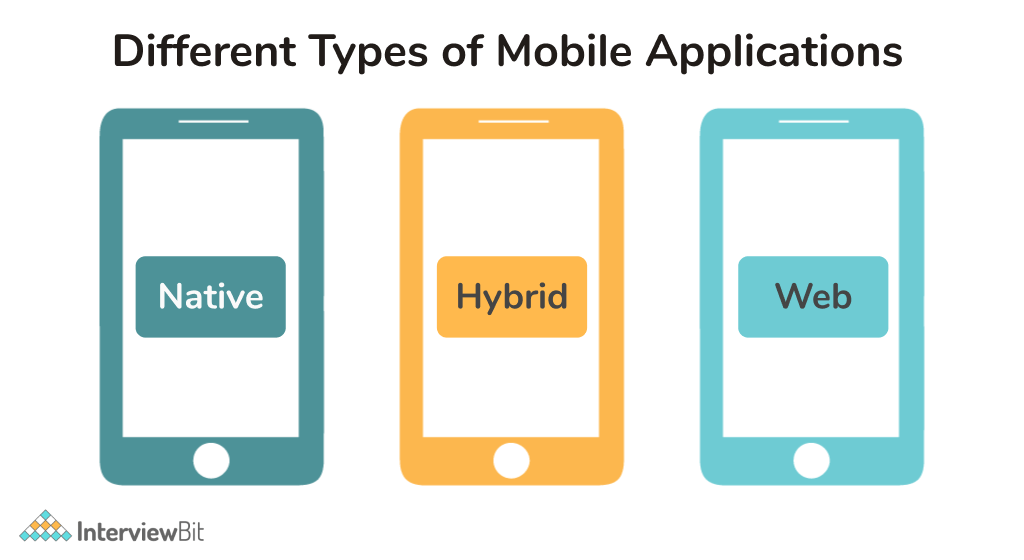
- Native Applications: A native application is a program written in a specific programming language (such as Objective C for iOS or Java for Android) and installed directly on the device, allowing it to take full advantage of all of the device's characteristics. Native applications can work offline and utilise the device's notification system. App stores (such as Google Play or Apple's App Store) are used to install native applications. Native mobile applications have a high level of performance and dependability. Temple Run, Candy Crush, and other native apps are examples.
- Web Applications: Web applications are mobile web portals that have been specifically created, adapted, and hosted for mobile devices. They are accessed using a URL on the mobile device's web browser. When HTML5 was released, people learned that they could have native-like functionality in the browser, and web applications became extremely popular. Device capability is not available in mobile web applications. Google.com, m.snapdeal.com, m.yahoo.com, and more websites are examples of web applications.
- Hybrid Applications: Web applications embedded in native applications that operate on the device and are created using web technologies are known as hybrid applications (HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript). Hybrid applications run inside a native container and render HTML and handle JavaScript locally using the device's browser engine (not the browser). A web-to-native abstraction layer gives you access to the device features like the accelerometer, camera, and local storage that aren't available in mobile web applications. A hybrid application is not limited to a single platform or mobile device. As a result, once constructed, it can run on any device. Flipkart, Facebook, Twitter, and other hybrid applications are examples.
19. When should you use a simulator and when should you use an emulator?
-
Case when we should use a Simulator: Simulators are typically used in software testing situations where the goal is to ensure that the application functions as intended when interacting with external applications or environments.
For example, you could wish to see if an application can communicate data to another application. Because the actual hardware configuration is unlikely to have much of an impact on data transfers for your program, a simulated environment will usually suffice. Simulated testing environments are also useful for ensuring that an application's interface shows properly across a range of screen resolutions. -
Case when we should use an Emulator: When you need to test how software interacts with underlying hardware or a combination of hardware and software, emulators come in handy.
For example, if we want to discover if a firmware update will cause issues with our software or not, we can find out with the help of an emulator. Alternatively, we could want to know how our program performs when run on multiple CPUs or with varying memory allocations. Emulators come in handy in these situations as well.
20. Difference between Emulator and Simulator.
Simulator: A simulator is used to simulate an environment with all of the software variables and configurations that will be present in the actual production environment of an application. Simulators do not try to replicate the actual hardware that will run the application in production. Simulators can be written in high-level programming languages because they merely construct software environments. For example, a car racing game application can be thought of as a simulator as it simulates a real car race.
Emulator: An emulator does try to replicate all of the hardware and software aspects of a real-world environment. In most cases, you'll need to develop an emulator in assembly language to accomplish this. Emulators might thus be thought of as occupying a midway ground between simulators and real-world gadgets. For example, a car simulator racing game can be thought of as an emulator. It provides the hardware aspects of car racing as well with the help of emulators.
- Emulators replicate both hardware and software features, whereas simulators solely simulate environment features that may be adjusted or created using the software. Emulators aren't a replacement for real-device testing since they don't always do a good job of simulating the hardware and software of a production system. They simply allow you to create an environment that is more similar to that of a real device.
- Emulators are somewhat slower as compared to simulators as emulators need to sense the movement of hardware devices, convert it into a digital signal, and then process them.
21. Mention the advantages and disadvantages of Appium.
Following are the advantages of Appium:-
- Appium is an open-source application, implying that it can be downloaded for free and it is simple to set up.
- It can be used to run automated tests on hybrid, native as well as web applications.
- To make Appium compatible with automation, you don't need to integrate any new agents in your application, unlike other testing solutions. It tests on the very application that will be uploaded to the App Store.
- Appium now has a new feature. Along with mobile application testing, it now supports desktop application testing for Windows.
- Appium is a cross-platform, open-source mobile testing solution that allows us to conduct cross-platform testing. As a result, you'll be able to test across a variety of platforms (single API for both Android and IOS platforms).
Following are the disadvantages of Appium:-
- There is no support for generating detailed reports of the tests executed.
- The tests are a little slow because they rely on the remote web driver.
- The fact that Appium uses UIAutomator for Android, which only supports Android SDK, API 16, or higher, is not a limitation, but rather an overhead. Appium, on the other hand, does not natively support earlier APIs. To support older APIs, it makes use of an open-source library called Selendroid.
- On a Mac OS device, only one iOS Script can run at a time, which implies only one test can be run at a time. We will need the same number of Mac machines if we wish to run our tests on numerous iOS devices at the same time. Organizing many Mac machines, on the other hand, would be costly.
Appium Interview Questions for Experienced
1. What are the tools used in Appium for debugging?
We generally use log data ( a log file is maintained wherein whenever an error occurs, it is logged into this file) to see the cause of the issue, where the failure is occurring. So for iOS – iPhone configuration utility & for Android Monitor.bat, etc can be used. If you give the developer the logs from these tools, they'll be able to figure out what's causing the problem quickly.
Useful Resources:
2. What are the basic requirements for writing Appium tests?
Following are the basic requirements for writing Appium tests:-
- Driver Client: Appium's driver client simulates the behaviour of a user in mobile applications. Appium tests can be built with the aid of a client library, which wraps the stages of a test and sends it to Appium over HTTP.
- Appium Session: Because appium tests are run within a session, it's crucial to set up an appium session first. Once the automation of a session has come to an end, it will be terminated and the user will have to wait for the next session.
- Desired Capabilities: In order to start an appium session, it's critical to design some parameters known as desired parameters. Platform version, platform name, device name, and many others are among these parameters. This also aids in defining the type of automation that the Appium server is expected to provide.
- Driver Commands: Appium provides the ability to build tests using a large and expressive set of commands.
3. Mention the tests which you cannot do with an emulator but can do it with a real device.
Following are a list of tests that we may conduct on a real device but is not possible in an emulator:-
- Testing for interruptions during phone calls and messages.
- Performance of the application when the battery is low.
- Effect of the application on battery usage.
- A scenario where the memory card is mounted or unmounted from the device.
- Testing involves the use of Bluetooth.
4. Do you think that automation testing can be a complete replacement for manual software testing?
No, automation testing cannot be a complete replacement for manual software testing. This is because the tools used are meant to execute tests once they are set up and proper automation requires as little human participation as feasible. As convenient as it is, it should not be used to replace manual testing; rather, it should be used for repetitive activities such as load testing, which requires thousands of virtual users. Engineers should not automate test scripts if they are only intended to run on a periodic basis, nor should they automate code reviews or bug testing for new software builds that may require human engagement to detect errors. To sum up, we can say that large-scale, repetitive jobs are better suited to automation.
5. Differentiate between Appium and Selenium.
Selenium: Selenium is an open-source (free) automated testing framework for validating web applications across multiple browsers and platforms. Selenium Test Scripts can be written in a variety of programming languages, including Java, C#, Python, and others.
Following are the differences between Appium and Selenium:-
Based on Usage:
- Appium - Appium is a popular open-source for automation testing, notably in native applications such as Android and iOS apps. It can also be used in hybrid applications that run in both Android and iOS environments. This type of automation testing assures that no systemic issues arise as a result of any specific patch installation once the app has gone live in production. It assures complete integration testing and avoids a significant amount of manual labour on the tester's part. By using Appium, users can easily avoid manually testing each and every feature of the entire application every time.
- Selenium - Selenium is a common automated testing tool that is built for any type of web application. It is compatible with all current popular browsers and operating systems such as Windows, Linux, and MACOS.
Based on Design:
- Appium - Appium is primarily intended as an HTTP server because it will handle any type of mobile app. However, it is primarily following or developing the same in node JS, rather than utilising standard Java or JS code. As a result, developers who want to utilise Appium for automated testing in any type of mobile app must first install Node JS on their system before using the Appium tool.
- Selenium - Selenium is primarily used for maintaining automation logic on web applications or webpages. It is created in such a way that it may interact with the application quickly and easily by using browser activities.
6. Differentiate between Appium and Calabash.
Calabash : Calabash is an automation framework for automating user interface acceptance tests. It works with a variety of mobile systems, including iOS and Android. This can be used to automate a variety of mobile applications, including native, mobile web, and hybrid.
Following are the differences between Appium and Calabash:-
| Basic | Appium | Calabash |
|---|---|---|
| Programming Languages Supported | Java, Python, JavaScript,.Net, Ruby, and all other major programming languages are supported by Appium. | The Ruby programming language is the only one supported by Calabash. |
| iOS mobile web page | It necessitates the creation of a custom safari application for automation. | Calabash does not support it yet. |
| Native iOS application | It requires only the iOS UI Automator. | It requires iOS instrumentation for this. |
| Hybrid iOS application | It necessitates the use of custom UI commands and the iOS UI Automator. | It necessitates the use of custom UI commands as well as an iOS framework. |
| Hybrid Android application | Only the Selendroid application is required. | Android instrumentation is required - calabash android. |
| Android mobile web application | It can be used to automate only the chrome browser. | It is not supported by Calabash. |
| Native Android application | Both Android UI Autometer and Selendroid are required by Appium. | Android instrumentation is required - calabash android. |
7. Differentiate between open source tools, vendor tools and in house tools.
- Open Source Tools: Open source tools are frameworks and apps that are free to use. Engineers construct this tool and give it free on the internet for other engineers, developers, or enthusiasts to develop and use, which is incredibly beneficial for aspiring developers.
- Vendor Tools: Vendor tools are created by companies that have a license to utilize their tools and codes. Technical support is accessible via the internet for these tools.
- In House Tools: In-house tools are the tools that a corporation develops for its own usage and self-development. They are never made available to the general population.
8. Differentiate between Appium and Robotium.
Robotium: Robotium is a testing framework for Android that automates test cases for native and hybrid apps. The developer can use Robotium to construct robust automatic Graphical User Interface (GUI) testing cases for Android applications. A developer might also design a functional, system, and acceptability test scenario, which would cover a wide range of Android activities.
Following are the differences between Appium and Robotium:-

- Appium is a cross-platform testing tool that works on both iOS and Android devices. Robotium, on the other hand, is limited to Android.
- Robotium only supports the Java programming language, but Appium supports a variety of languages.
- The Appium tool does not require any application source code or libraries, whereas the Robotium tool does.
- Appium can test native, web, and hybrid mobile apps, whereas Robotium can only test native and hybrid mobile apps.
- Many frameworks, such as Selenium, are supported by Appium. Robotium, on the other hand, is incompatible with Selenium and many other frameworks.
- You don't have to reinstall Appium every time you make a little modification. However, a simple change in Robotium code necessitates a complete rebuild.
9. Differentiate between Appium and Selendroid.
Selendroid: Selendroid is a cutting-edge test automation framework for testing native and hybrid Android mobile apps. The test is created using the Selenium 2 client API and is driven by the user interface of a mobile or web app. Selendroid is a dynamic mobile testing framework that can be used on emulators as well as real Android smartphones, with the option of integrating as a node in Selenium Grip for parallel testing and scaling.
Following are the differences between Appium and Selendroid:
- Appium is an open-source automation solution that works on both iOS and Android, whereas Selendroid is an Android-only test automation framework.
- A minor modification in Appium does not necessitate reinstalling the application. However, Selendroid requires the application to be reinstalled even after a minor modification..
- Appium has a large and active community of active developers, whereas Selendroid does not have one.
- Appium is compatible with a wide range of frameworks and languages. Selendroid, on the other hand, works with Jenkin and Selenium.
- Appium does not necessitate the use of application source code or libraries, unlike Selendroid does.
- Appium supports all Android APIs. Appium uses UIAutomator for tests that run on APIs greater than or equal to 17, and Selendroid for tests that run on older APIs. Selendroid, on the other hand, has different versions corresponding to the different versions of the Android APIs.
10. Explain how Appium works.
When we install Appium on our PC, it also installs a server that exposes the REST API. It accepts commands and connection requests from the client and executes them on iOS or Android devices. It responds to HTTP requests with HTTP responses. It runs the user interface of the app using a mobile test automation framework to perform requests. As an example -
UIAutomator is used for Android API 16 or higher, while Selendroid is used for Android API 15 or below. Apple Instruments is used for iOS.
Working of Appium on Android:
Appium sends the command to a UIAutomator script running on the device on Android. UIAutomator is an Android native UI automation framework that allows you to run Junit test cases straight from the command line on the device. Despite the fact that it is written in Java, Appium can be run from any WebDriver enabled language.
Android makes use of bootstrap.jar, a TCP server. It's used to deliver test commands to an Android device, which UIAutomator then executes.
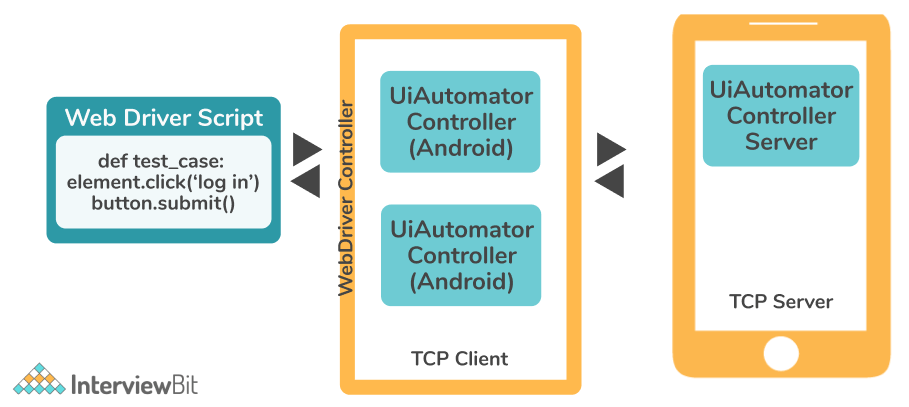
In the above image, we can clearly see the architecture of Appium used for running on Android devices.
Working of Appium on iOS:
As Android uses UIAutomator, iOS uses UIAutomation. Similar to the Android, Appium proxies the command to a UIAutomation test case running on the Mac instruments environment. Apple provides this application "instrument" that performs various activities like building, profiling, and controlling iOS apps. On the other hand, it also has an automation component where you can write commands in JavaScript. It uses UIAutomation API to interact with Application UI. Appium uses the same libraries to automate iOS Apps.

In the above image, we can clearly see the architecture of Appium used for running on iOS devices.
Appium MCQ Questions
When should you choose automation testing over manual testing?
Which of the following is a type of mobile application testing?
Which of the following applications can be used with Appium for automation?
Which of the following is an advantage of using Appium for mobile automation testing?
What does AAPT stand for?
Which of the following is not a basic requirement for writing Appium tests?
Which of the following is true about Appium Doctor?
Which of the following languages is Appium written in?
Which of the following Selenium commands can be used to work with Appium?
Which of the following is true about Appium?












 Download PDF
Download PDF



















