VMware Interview Questions


About VMware
Incorporated in 1998, VMware is a cloud computing and virtualization technology company based in Palo Alto, California. The company has offices around the world and has a global presence. The company offers advanced cloud services through its partnerships with Cisco Systems and Amazon Web Services. It is known worldwide for its vSphere VMware Hypervisor, which allows any architecture, whether x86 or x64, to be virtualized. Performance, reliability, flexibility, and scalability are at the heart of its engineering work.
Working with VMware allows you to collaborate with a global community that is working together to address the vital technological challenges of today. The business is driven by the values of innovation, positive leadership, and respect. VMware's incredible culture and its principles have contributed greatly to the growth of the company, and a great management team and work-life balance make it one of the best companies to work for.
Despite having a desire to get a job with VMware, many of you are unsure what to expect in your interview. The purpose of this article is to let you know what an interview at VMware looks like. If you're about to take a VMware interview, these tips and VMware Interview questions will help you succeed.
VMware Interview Questions for Freshers
1. Explain what you mean by Port-group.
As the name suggests, port groups are groups of virtual ports on our virtual switch. In general, the port group provides a stable anchor point for virtual machines connected to labeled networks by aggregating multiple ports into a single configuration. Every port group is assigned a network label, which is unique to the host. VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) tags, for example, are shared by each port group member.


 Real-Life Problems
Real-Life Problems
 Prep for Target Roles
Prep for Target Roles
 Custom Plan Duration
Custom Plan Duration
 Flexible Plans
Flexible Plans
2. Explain the different types of virtualization available.
Virtualization generally enables your organization to run many processes at once with fewer physical infrastructures, leading to greater efficiency and cost savings. VMware manages different types of virtualizations, each having different uses in the industry.
Types of virtualization-
- Server Virtualization: It is a type of virtualization where many virtual machines (VMs) run on one physical server. Since you do not have to buy new servers or expand your server room, you save floor space and money. Server virtualization is offered by a few well-known providers, such as vSphere, XenServer, Hyper-V, and RedHat.

- Network Virtualization: It refers to the process of combining all the physical network components into one virtual network. A virtual network can be composed of NICs, switches, VLANs, network storage devices, virtual network containers, and network media. This type of virtualization has the primary function of eliminating physical network device dependencies. One of its examples includes VMware NSX.
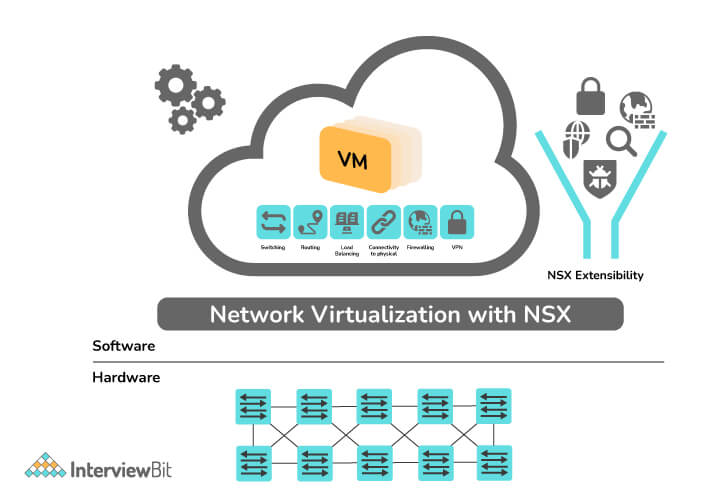
- Application Virtualization: The process involves virtualizing and hosting applications on a server so that end users can have access to them on their devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets. The app can be accessed via any Internet-connected device, so you don't have to log in to a desktop at your office to use it. Its example includes VMware ThinApp, Citric XenApp, etc.

- Desktop Virtualization: Often called OS virtualization or VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure), desktop virtualization is the process that enables you to run or deploy multiple virtual desktop OS on a physical server. The user may access his or her virtual desktop from anywhere since it is stored on a remote server. In this way, the need for individual CPUs is eliminated. Its example includes VMware Horizon View, Citrix Xen Desktop, etc.

- Storage Virtualization: Using storage virtualization, multiple network storage devices can be combined into a single storage device/array by pooling their physical storage. It provides an easy way to manage storage and ensure consistent performance. Its example includes vSAN.

3. Explain VMKernel and its importance.
VMware's VMkernel is a high-performance operating system that runs directly on the ESXi host. VMkernel generally acts as an interface between VMs and the physical hardware of the system and is referred to as microkernel by VMware since it runs on bare metal, directly on VMware ESX hosts. In addition to providing hardware abstraction and operating system (OS) services, VMKernel allocates memory and schedules CPUs. In addition, it handles services such as vMotion, Fault Tolerance, NFS, and iSCSI. In order for VMs to communicate with ESXi, the VMKernel is vital.
4. Write four core elements of the VMkernel networking layer.
VMkernel networking enables vSphere to interact with the outside world. It consists of four core elements:
- Virtual SAN
- Fault Tolerance
- Science storage
- VMotion
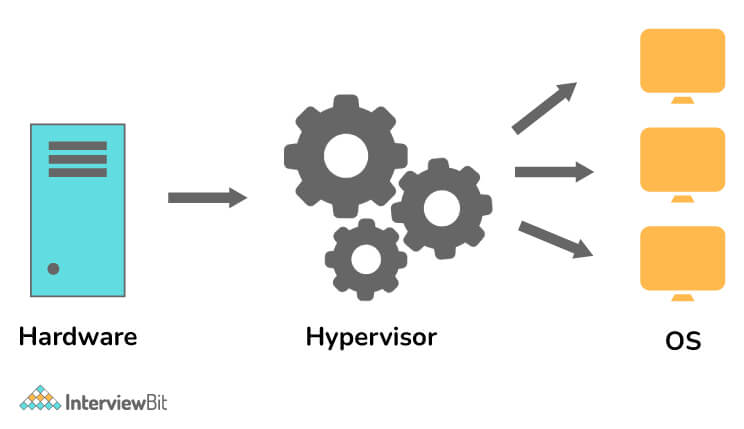
5. What do you mean by Hypervisor? Write its type.
Hypervisors, also known as VM monitors or VMMs, are software that creates and runs virtual machines (VMs) as well as also manages and allocates resources to them. By sharing its resources in virtual ways, such as memory and processing, a host computer can support multiple guest VMs. The special feature of a hypervisor allows several virtual machines to run on a single physical server. As a result, it reduces:
- Space efficiency
- Energy usage
- Server maintenance requirements.
Types of Hypervisor-
- Type-1 Hypervisor (also known as Bare Metal or Native Hypervisor)
- Type-2 Hypervisor (also known as Hosted Hypervisor)
 Learn via our Video Courses
Learn via our Video Courses
6. What do you mean by ESXi?
ESXi (Elastic Sky X Integrated): ESXi (formerly ESX) is a virtualization platform developed by VMware for deploying and managing virtual machines. With ESXi, you get a very secure OS architecture that includes and integrates essential OS components like the Kernel. For efficiency, reliability, and performance, it's the leading choice. ESXi partitions hardware to consolidate applications and reduce costs by directly accessing and controlling underlying resources. It is a hypervisor that makes use of bare-metal virtualization technology.
7. Explain NFS and VMFS.
- NFS (Network File System): ESXi hosts use this file-sharing protocol to share files with NAS devices. Storage devices such as NAS connect to networks and enable ESXi hosts to access files.
- VMFS (Virtual Machine File System): In VMware vSphere, it is a block-level file system that stores virtual machine files. In vSphere 6.0, it can also store large files up to 64TB in size.


 Real-Life Problems
Real-Life Problems
 Detailed reports
Detailed reports
8. Explain the .vmdk file.
Virtual Machine Disk (VMDK) is an open file format by VMware which is used to store the content of virtual hard disks. In vSphere 5.5 and later versions, it can be up to 62 TB in size. Earlier, VMware products used the extension .dsk to store content or data or virtual disk files.
9. Name some of the VMware products.
VMware offers the following products:
- VMware Mirage
- VMware Pivotal Container
- VMware Photon Platform
- VMware Thinapp
- VMware vCloud NFV
- VMware vCloud NFV Openstack
- VMware vRealize
- VMware vRealize Operations, etc.
10. What are the VMware components?
VMware infrastructure consists of the following components:
- VMware ESX Server
- VirtualCenter Server
- VMware Infrastructure Client (VI Client)
- VMware Infrastructure Web Access (VI Web Access)
- VMware Virtual Machine File System (VMFS)
- VMware Virtual Symmetric Multi-Processing (SMP)
- VMware VMotion and VMware Storage VMotion
- VMware High Availability (HA)
- VMware Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS)
- VMware Consolidated Backup (Consolidated Backup)
- VMware Infrastructure SDK
11. Explain VMware DRS.
DRS (Distributed Resource Scheduler), as the name suggests, provides a way to schedule and balance resources across a vSphere environment. Through the use of clusters and resource pools, virtual environments are able to automatically balance available resources across hosts. DRS uses VMware HA (High Availability) to move VMs from one host to another to ensure that resources are evenly distributed among them.
12. What is the importance of virtualization?
A virtualization process creates a virtual version of a physical device, such as a server, storage device, network device, on a physical host. On a single machine/server known as an ESXi (ESX integrated) host, several virtual machines, as well as multiple operating systems and applications, can be operated. It has the following advantages:
- Increasing IT agility, flexibility, and scalability while reducing costs.
- Increased workload mobility, performance, and resource availability.
- Automated operations that save time.
- Simplify IT management and make it less expensive to operate.
13. Write three port-groups that are configured in ESXi networking.
The following are the three port-groups configured in ESXi networking:
- Virtual Machine Port Group: They are used for Virtual Machine Network.
- Service Console Port Group: They are used for Service Console Communications.
- VMKernel Port Group: They are used for vMotion, iSCSI, NFS (Network File System) Communications.
14. Explain iSCSI storage.
Generally, iSCSI SANs consist of an iSCSI storage system, which houses one or more storage processors. Communication between the host and array occurs over TCP/IP protocol, and ESXi hosts are configured with an iSCSI initiator. Such an initiator is either hardware- or software-based. The hardware-based initiators can be dependent or independent; the software-based ones are called iSCSI software initiators.
15. What is the meaning of VVol?
vSphere 6.0 introduces the concept of Virtual Volume, also known as VVol, for managing virtual disks. Whenever a virtual disk is created in a virtual environment, VVol is automatically created. At the virtual disk level, it enables array-based operations.
16. Explain Cluster.
In VMware, the cluster is defined as a logical grouping of multiple ESXi hosts. It lets you add and remove hosts from a cluster. HA and DRS are also provided on the cluster.
17. Explain cold and hot migration?
- Cold Migration: This is the process of migrating a powered-off VM, including its configuration and data, from a single host to another. One can migrate VMs manually or set up a scheduled task to perform cold migration.
- Hot Migration: This is the process of migrating a powered-on VM from a single host to another. It is also known as live migration because there is no need to shut down the VM.
VMware Interview Questions for Experienced
1. What is VDI?
With VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure), users can host a desktop operating system (OS) on a server and access VM-based desktops remotely from different devices and locations. VDI is a type of IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), which can be run in a private or public cloud. When VDI is used, the end-user can access his or her desktops via a device called a thin client.
2. How many CPUs can be used for a VM in FT in vSphere 7.0?
In VMware vSphere 7.0, up to 8 vCPUs can be used with the VMware vSphere Enterprise Plus license.
3. Explain FT logging traffic.
For VMware FT, fault tolerance logging traffic is considered as the second network requirement. For continuous data syncing between primary and secondary VMs, Fault Tolerance applies FT logging. Additionally, this is a VMkernel connection type used to move nondeterministic events from primary to secondary VMs.
4. What is the difference between vSphere and vCenter?
- VMware vSphere: It's an enterprise-scale virtualization platform that lets you build a reliable and resilient infrastructure to meet pretty much any business need while staying within your budget. Vsphere adds important capabilities to data center infrastructure that prevent unplanned downtime and can completely eliminate maintenance and storage downtime.
- VMware vCenter: It is a centralized platform used to manage virtual infrastructure. From a single console, you can control all your hosts and virtual machines, enhancing visibility and preventing errors. Even if you are managing a large-scale environment, vCenter Server lets you optimize routine operations and daily tasks. As a result of this functionality, you are able to get a detailed understanding of how your environment is configured.
5. Will FT (Fault Tolerance) work if the vCenter server goes down?
Fault Tolerance on a VM can only be enabled through the vCenter Server. FT does not require vCenter to be online once configured. Due to this fact, no FT failure between the primary and the secondary will occur when vCenter is down.
6. What is the use of vMotion?
VMware's VMotion technology enables you to migrate active virtual machines from one ESX-host to another without disrupting service or functionality. During this process, there is zero downtime, constant service availability, and overall transaction integrity. vMotion technology plays a key role in creating a dynamic, automated, and self-optimizing data center and provides great flexibility for virtual environments. Ensure that both hardware and software requirements are met by the cloud provider. The compatibility requirements are reduced if powered-off VMs are migrated.
7. What will happen if vMotion fails?
A virtual machine will not be migrated if the target host does not have enough memory i.e., vMotion fails. This can be fixed by moving the VM to another ESXi host providing guaranteed memory, or by reducing the virtual machine's memory reservation.
8. Explain Promiscuous mode.
A promiscuous mode is network security, monitoring, and administration method that allows any network adapter configured on a host system to access all network data packets. You can specify it at the virtual switch or port group level in vSphere ESX/ESXi. Essentially, promiscuous mode is a method of monitoring (sniffing) network traffic. You have two options: accept or reject. Additionally, all communication will be visible to all virtual machines if the promiscuous mode is set to accept.
9. There are several features such as DRS (Distributed Resource Scheduler), SMP (Symmetric Multi-Processing), VMotion, etc., but why do we need ‘HA’?
VMware HA is critical for us since we need uninterrupted service. Let's suppose that one of the ESX servers in the cluster crashes suddenly for some reason. What would happen to the virtual machines running on that server? Do they continue running or are they falling? Likewise, they go down too. Thankfully, VMware HA allows you to restart these VM's on any other ESX server in the same cluster as soon as they fail.
10. What is the importance of snapshots in VMware?
VMware snapshots allow you to quickly and easily save the state of a VM before making changes. A snapshot is taken when upgrading or installing software. In VMware snapshots, the current state of the virtual machine is preserved, so after testing, the machine can be quickly reverted to the desired state. After a specific task is completed, a snapshot should be removed to improve performance.
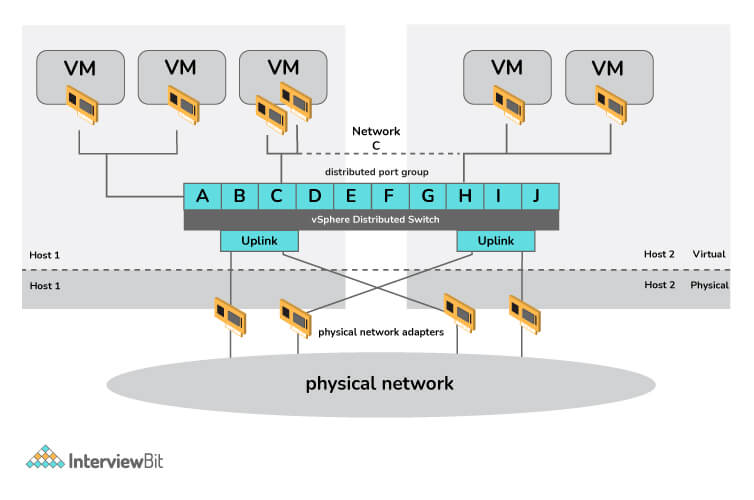
11. What are vSS and vDS?
To connect virtual machines, VMware vSphere offers two types of virtual switches. vSphere administrators can control the traffic between VMware virtual machines using either type of virtual switch.
- vSphere Standard Switch (VSS): VSS is the default virtual switch when ESXi is installed. The switch allows VMs installed on one physical host to communicate with one another. The switch controls how a VM communicates with another VM on the same physical server, just as a physical switch would.

- vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS): It acts as the single switch in a virtual environment and provides central provisioning, administrative, and monitoring capabilities for virtual networks. Additionally, it supports advanced networking features in VMware vSphere.
12. What do you mean by VMware HA and VMware FT? Difference between them.
- VMware HA (High availability): It generally works on Cluster Level. By pooling VMs and the hosts they reside on into a cluster, VMware HA provides high availability for VMs. VMs running on a failed host are forced to be restarted on alternate hosts.
- VMware FT (Fault Tolerance): It generally works on VM Level. In this, a secondary VM is created and maintained that is identical to the primary and can replace it when the ESXi host fails to provide continuous availability of VMs. A complete copy of a VM is made, including storage, computation, and memory. To configure FT, a 10GB NIC is recommended.
Difference between VMware HA and VMware FT-
- While VMware HA is enabled per cluster, VMware FT is enabled per VM.
- VMware HA works on cluster level whereas VMware FT works on VM level.
- An HA system will restart and power on VMs on another host in the event of a failure, while an FT system will activate the second copy in case of a loss of the primary host. By providing fast backup and continuous availability, it reduces downtime.
13. What do you mean by vCloud Suite?
vCloud Suite is often described as an enterprise-grade cloud and management solution. It is a collection of multiple VMware components to build and provide a completely integrated cloud infrastructure, that includes virtualization, software-defined datacenter services, disaster recovery, application management, etc.
14. Why use VMware Workstation?
VMware Workstation is software that allows users to run multiple operating systems on the same host computer. Virtual machines are capable of running one instance of any operating system such as Microsoft, Linux, etc.
Here are three reasons why VMware workstation is useful:
- Allows the user to run more than one operating system on the same computer.
- It saves the current OS configuration as virtual machines.
- You can work across different OSs without switching.
15. Why use virtual machines instead of original hardware?
In the absence of virtualization, it would be impossible to run multiple operating systems at once, such as Windows and Linux. Virtual machines serve mainly the purpose of running multiple operating systems concurrently on a single piece of hardware. Splitting a physical server into multiple units reduces the need to invest in additional units. You can also use VMs to enable rapid disaster recovery and automatic backups of your data.

16. What is the major advantage of VM running under a type 1 hypervisor than type 2 hypervisor?
- Type-1 Hypervisor: It acts as a lightweight OS and runs directly on the host system. A base server OS is not required, and direct hardware access is available. Its example includes VMware ESXi, Citrix XenServer, etc.
- Type-2 Hypervisor: It cannot run directly on the underlying host system, but can run as an application layer on a host system, similar to other computer programs. Its example includes VMware player or parallel desktop, VMware Server, etc.
Advantages of using Type-1 over Type-2 Hypervisor:
It is more secure to use type-1 hypervisors since they do not rely on the underlying OS, unlike type-2 hypervisors. The type 2 server also loses some efficiency, performance, and speed due to this dependency. So, if you're under attack, a type-1 hypervisor will give you better protection than a type-2 hypervisor.
17. What do you mean by RDM?
The Raw Device Mapping (RDM) files are contained in VMFS and act as proxies for raw physical devices. This feature enables VMware's virtual machines (VMs) to access logical unit numbers (LUNs) directly. This eliminates the need to use the virtual machine file system (VMFS) because the LUN can be formatted using any file system like NTFS (New Technology File System). It is generally beneficial for cluster configurations including VM-to-VM, physical-to-VM, or SAN (Storage Area Network) snapshots. But it has some limitations, including the inability to map disk partitions and possibly not working with direct-attached block devices.
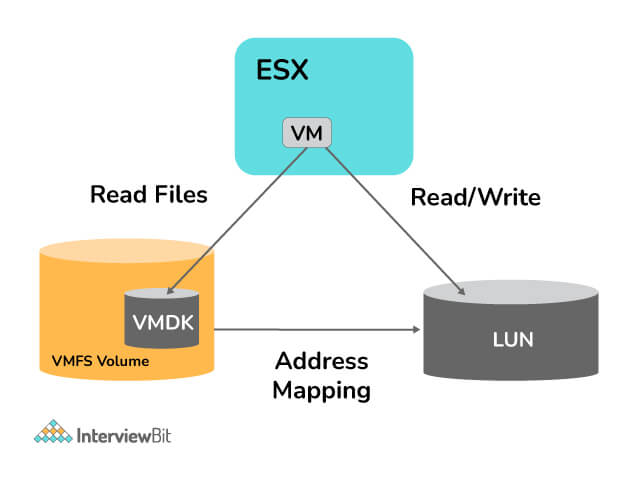
The figure above shows that an RDM disk exists as an address mapping file on a VMFS volume. This mapping file acts as a symbolic link between a VM's access to an RDM disk to LUNs.
18. What is clone and template in VMware? Differentiate between them.
- VMware clone: It is an identical copy of a VM (called parent VM (Virtual Machine), since it is the one from which you made a clone). MAC addresses and UUIDs for both cloned and parent VM, however, will be different. Any changes to the cloned VM will not impact the original VM or parent VM (and vice versa).
- VMware template: It is a golden image or a master copy of Virtual Machine that is capable of creating and provisioning virtual machines. It can later be used to make many clones.
| Clone | Template |
|---|---|
| An exact copy of an existing virtual machine that works independently. | A master copy of a VM with basic configurations, although it cannot work independently. |
| You can turn it on/off. | You cannot turn on/off or edit a template. |
| It is not possible to convert a cloned VM back to a parent or original VM. | The template can be converted back to a Virtual Machine and updated with the latest configuration before being converted back to the template for use in future VM deployments. |
| They are ideal for test environments or disaster recovery environments. | For deployment of mass virtual machines in production environments, the template works well. |
| For large deployments of VMs, it is not recommended. | When deploying large numbers of VMs, it is recommended. |
| The VM that is powered on can be cloned. | A powered-on VM cannot be used to create a Template. |
Tips to Prepare for VMware Interview
1. VMware Interview Preparation
- The Generic Tip: Using online IDEs and platforms such as HackerEarth, Hacker Rank, LeetCode, Code Chef, and so on, is always a good idea for practicing coding questions. Since it is critical to code your solution accurately and in a timely manner, use the programming language you're most comfortable with.
- Speak what you believe: At the moment, the point is how to give them what they are looking for. The interviewer will have no prior knowledge of your abilities, yet they will attempt to assess your years of education in 30–40 minutes. Even if you write the correct solution to the problem without saying anything, the interviewer is unlikely to deduce anything about your mental state. The only way out is to say exactly what you're thinking because your voice is the only method for them to understand what and how you are thinking. So, you must express yourself at every stage of your thought process. Even if you believe your method may be incorrect, just say so. Don’t ever hesitate.
- Prepare Well: The technical round may include a number of questions. Prepare all in advance. Make sure you have knowledge of DSA. Basic questions related to coding, OS, process synchronization, recursion and iterative techniques, sorts, searches, and traversals should also be considered as well. Become well-versed in fundamental subjects such as operating systems, databases, and computer networks. Reading prior interview experiences and questions will also improve your insight into the interview process.
- Ask for Hints: Don't pester the interviewer with demands for hints. In fact, try if you can find and fix the issues yourself. And if you feel absolutely stuck, instead of continuing to flounder, simply ask for help. It demonstrates that you acknowledge your insufficiency of knowledge, but do not immediately give up trying to learn. Make use of the hints you've been given. In most cases, the interviewer is familiar enough with the question to recognize which tips would help you next if you get stuck.
- Confidence is crucial: No matter how frightened you are, face the interviewer with confidence. The confidence you exude isn't for you; it's for the interviewer to feel comfortable enough to hire you. You must persuade her/him that you are a valuable asset to the firm.
- Prepare generic questions for HR or Managerial round: Find out online what general HR questions you might be asked during your interview. Never know when someone will ask you, "Why did you choose VMware?" or "Why not another company?". It's, therefore, a good idea to learn a bit about the company before your interview.
- Ask questions: Be sure to keep the flow two-way. If you have doubts, you should voice them to the interviewer. Your willingness to join will be apparent to the interviewer if you do this.
FAQ
1. How many rounds are there in VMware Interview?
Generally, 4-5 rounds are there in the VMware Interview process:
- Online Assessment
- Technical Rounds (2-3)
- Managerial Interview
- HR Interview
2. How to get a job in VMware?
As a software company, VMware is committed to the notion of equal employment opportunities for all employees, as well as to providing a non-discriminatory and harassment-free workplace. At VMware, employees are hired based on business needs, job specifications, and individual qualifications. All applicants are encouraged to apply, whether they are freshers or experienced. Therefore, if you want to get hired, you must prepare thoroughly. Start by researching about the company, their interview process, tips on how to prepare for the interview, and then prepare accordingly. If you would like to apply, you can visit the career portal and apply directly or you can ask for a referral.
3. How long does the offer process take at VMware?
It will take approximately 2-4 weeks to receive an offer letter following the final interview.
4. Why do you want to join VMware?
As a VMware employee, we will be a part of a global community of innovators and leaders that solve technical challenges together. Here, employees are surrounded by an environment filled with possibilities and are always encouraged to bring new ideas to life. Every day, employees are challenged to innovate in everything VMware does.
5. Is VMware Interview hard?
The amount of time and effort you put into preparing for an interview can greatly affect how tough it is going to be. VMware interviews usually consist of easy to medium level questions, however, this depends on the individual. Since the number of rounds varies from 4-5, some candidates may find it intimidating. I assure you it is worth the effort if you join.
6. What is the role of VMware admin?
Virtual machines, hardware, and servers are familiar terms to most VMware admins. They use a specific VMware environment such as vSphere to create and install computer infrastructure, including hardware, servers, and virtual machines. Maintenance and troubleshooting are a major part of their job.
The following are some of the roles of a VMware administrator:
- Managing the host's storage and VMs
- Maintain and upgrade the Virtual Center
- Simplify template management and cluster management
- Coordinate with vendors
- VM Troubleshooting, etc.
Useful Resource
Multiple Choice Questions
Which of the following type of virtualization enables you to run or deploy multiple virtual desktop OS on a physical server?
How does VDI benefit you?
What tool does one use to convert a physical machine to a virtual one?
Which of the following is the latest version of vSphere?
VMFS stands for __.
Are any of the following types of virtualization?
Which of the following is true about RDM?
Which software allows you to run multiple operating systems on one physical server?
What is VMware ESXi?
Which of the following is a type-2 hypervisor?
FT stands for __.












 Download PDF
Download PDF



















