How does Binary Search Work?
Binary search works by repeatedly dividing the array into two halves that can contain the given target element, till the search area is limited to just one element. The necessary condition for binary search to work is the array needs to be sorted
Binary Search Example:
Given a sorted array, find if element 2 is present in the array.
Step 1: The given array:

Step 2: Consider two pointers, low = 0 and high = N - 1, where N is the size of the array.
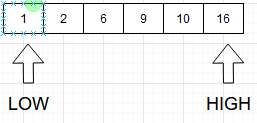
Step 3: Find the mid, i.e. mid = (low + high) / 2. Here, mid = (0 + 6) / 2 = 3.
 Step 4: Now, check for three conditions:
Step 4: Now, check for three conditions:
- Compare if A[mid] = 2
- Compare if A[mid] > 2
- Compare if A[mid] < 2
- It can be observed that, A[mid] = 9, which is > 2, therefore, we shift, high = mid - 1.
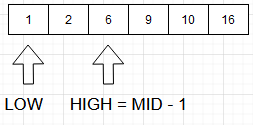
Step 5: If A[mid] < 2, shift low = mid + 1.
Step 6: Repeat Steps 3 to Step 5, until the search area is limited to just one element i.e. low = high.
Step 7: The value 2 is found.
Binary Search Implementations
Binary Search can be implemented in mainly two ways:
- Recursive method
- Iterative method
Let us first discuss the Recursive method.
Recursive Method
int bSearch(int arr[], int left, int right, int target) {
if (right >= left) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target)
return mid;
if (arr[mid] > target)
return binarySearch(arr, left, mid - 1, target);
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, right, target);
}
return -1;
}
class BinarySearch {
int bSearch(int arr[], int left, int right, int target) {
if (right >= l) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target)
return mid;
if (arr[mid] > target)
return binarySearch(arr, left, mid - 1, target);
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x);
}
return -1;
}
}
def bSearch(arr, left, right, target):
if right >= left:
mid = left + (right - left) // 2
if arr[mid] == target:
return mid
elif arr[mid] > target:
return binarySearch(arr, left, mid-1, target)
else:
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, right, target)
else:
return -1
Time Complexity :
- Best Case Complexity : O(logN)
- Average Case Complexity : O(logN)
- Worst Case Complexity : O(logN)
Iterative Method
int bSearch(int arr[], int left, int right, int target) {
while (left <= right) {
int m = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[m] == target)
return m;
if (arr[m] < target)
left = m + 1;
else
right = m - 1;
}
return -1;
}
class BinarySearch {
int bSearch(int arr[], int left, int right, int target)
{
int left = 0, right = arr.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int m = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[m] == target)
return m;
if (arr[m] < target)
left = m + 1;
else
right = m - 1;
}
return -1;
}
}
def bSearch(arr, left, right, target):
while left <= right:
mid = left + (right - left) // 2
if arr[mid] == target:
return mid
elif arr[mid] < target:
left = mid + 1
else:
right = mid - 1
return -1
Time Complexity :
- Best Case Complexity : O(logN)
- Average Case Complexity : O(logN)
- Worst Case Complexity : O(logN)
Walkthrough Examples :

















 Video Courses
Video Courses












